Methods
- 19 dogs from random owners from Linköping
- All dogs went through both test (traditional CJB & novel CJB)
- Their personality traits were assessed by using the DPQ elaborated by Jones (2008) because of its impact on the CJB responses (Barnard et al., 2018)
Traditional CJB (tCJB)
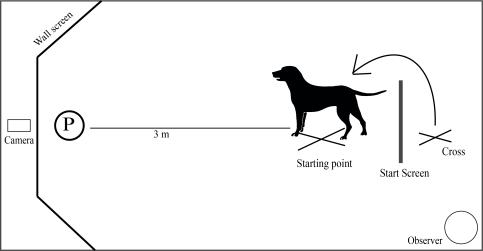
- For the tCJB, a location ambiguity test was used. The principle is to associate a specific location (ex: right side) to a reward and another location (ex: left side) to no reward, so a “negative” location. Then a scale of different location within the two previous spots (left and right sides) is settled (ex: near-left side, middle, near-right side), and these within locations are not rewarded and are being ambiguous. But for this tCJB only a middle probe location was chosen.
- The learning criterion for this study has been inspired from Mendel et al. (2010) study and was such that the latency for the preceding three rewarded trials at least 1s faster than the preceding three unrewarded trials. Each trial was terminated once the dog ate the treat or reach the time limit of 20 s.
- This test was consisting of a Warm-up phase, Training phase and Testing phase
- Warm-up phase: The owner goes with the dog to the bowl and points at it (x3), then the owners stays on the starting point and point at the bowl (x3). This sequence is repeated for the other location.
- Training phase: This phase started right after the warm-up phase and with the dog starting from the starting point. The dog was given first 2 times the rewarded side and then 2 times the unrewarded side. After, a pseudo-random order was given and as a rule, no more than two times in a row the same trial valence.
- Testing phase: The testing phase started immediately after the dog has reached the learning criterion. For this phase, the following fixed order was used: + + - - + + - - + + - - + + A A.
“A” being the ambiguous cue, the same bowl positioned equidistantly to the right and left side. The protocol is then the same one used during the training phase.
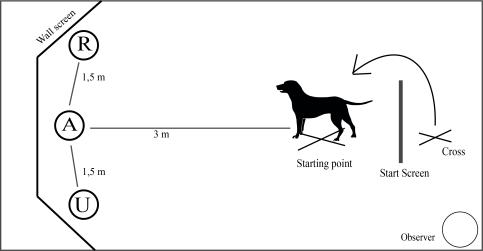
Novel CJB (nCJB)
For this method, no learning criterion was required and there was no time limit for each trial, which ended when the dog ate the treat.
The picture display was 3 meters away from the starting point. The pictures (size A3) were fixed onto the back wall with a clothespin at ground level with the bowl being in front of the picture (Figure 3). Pictures of a smiling human face (positive cue, R) were display on front of the dog, either female face or male face depending on the main owner’s sex. The same aggressive dog picture was used for every dog (negative cue, U). The ambiguous cue (A) was a digital morph picture made by combining the human smiling face (male or female) and the aggressive dog face with the software SqMorph (Figure 2).
Each dog went through the same fixed order consisting of 9 probe exposures:
+ - M + - M + - M.

Responsible for this page:
Director of undergraduate studies Biology
Last updated:
