Here I will present you the methods I used to assess 1) Cognitive bias, 2) Short-term memory, 3) Long-term memory, 4) Social reinstatement.
Animals
Hatchery treated chickens (HC): Those chicks went through the entire incubation, hatching and post-hatching procedure at the commercial hatchery. Once hatched, each trail of the incubator was placed on a conveyor belt on which the eggshells were removed by hand. Manual sex sorting was then processed on another conveyor belt by using wing inspection. Via a conveyor belt, the chicks were then transported to a vaccination station, which consisted in a needle attached to the table. Finally, chicks were separated and counted automatically before being dropped into transport boxes. Chicks were then transported to Linköping University which required 3.5 hours by car.
Control chickens (CC): Those chicks were incubated and hatched in Linköping university but come from the same place as the hatchery chicks. After hatching, the chicks were placed in rearing pens, in the same building as the incubators and hatchers to limit additional transport and were used as control animals.
1) Cognitive bias
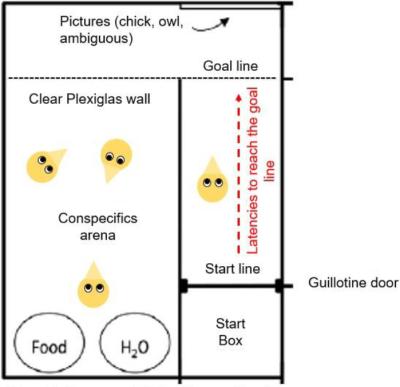
The apparatus consisted of a start box followed by a straight alley adjacent to a conspecific area. The alley ended by a goal line facing the picture that were presented to the chicks.
Cognitive bias was assessed by observing the start latencies (the time the chick took to completely exit the start box) and the goal latencies (the time the chick took to reach the goal line) of chicks toward different goal images: a mirror (reflecting the individual that was tested), a silhouette of a chick, of an owl and silhouette of an ambiguous morph featuring 50 % of characteristics of chick and 50 % of the owl. The chick silhouette is supposed to represent a positive stimulus followed by a short latency, while the owl is expected to be perceived as a predator, leading to a longer latency. Approach towards the ambiguous morph is expected to reflect cognitive bias of an individual. If an individual is optimistic, it should perceive the ambiguous morph as a potential conspecific and shows shorter latencies than if it perceives it as a predator (indicator of a pessimistic state of mind).
2) Short-term memory

In order to investigate short-term memory I used a experiment similar to a delayed matching-to-sample protocol.
This experiment’s purpose was to evaluate and compare short term memory between the CC and HC group. One chick was presented with conspecifics either on right side or on the left side of an arena. After a retention delay during which it couldn’t see the conspecifics, the chick had to recall on which side it saw the conspecifics.
The tested chick was kept during one minute in the start box while two pieces of dark fabric were hiding the transparent screens and therefore the view of the conspecifics. One of the fabrics (either the left or right) was taken off, enabling the chick to see its conspecifics behind one of the screens for 30 seconds. The fabric was placed back for 10, 30, 60 or 120 seconds depending on the moment of the experiment. After this delay, the door was opened, and the chicks was free to explore the arena for two minutes maximum. During those two minutes, the first choice made by the chicks was recorded: if the chick went to the side that was previously without the fabric, a correct choice was recorded. If the chick went to the other side an incorrect choice was recorded. If the chicks did not make any choice (cf: the chick stays in the start box or do not reach the first partition) a null choice was recorded.
3) Long-term memory
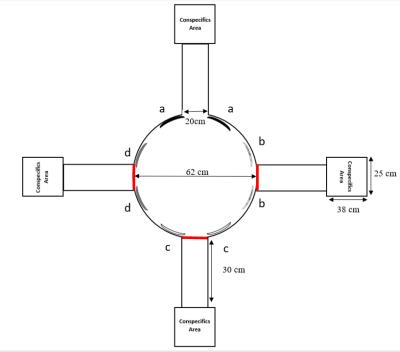
In order to assess long-term memory in chicks we used a circular area, surrounded by four arms that all leaded to conspecifics pen. A tested chick was placed in the middle of the arena, and three doors closed the access to the arms, while one door was always open, allowing the chick to cross the arm and reach the conspecific pen. All doors had visual cue on their side. The goal was that the chick could remember which door was always open, using possible the visual cue. For this, I used a training session with 5 consecutive trials in which the same door was open. Then, I tested the chick on more time either one hour or three hours after the trial session. In both sessions, the time to find the correct entrance was recorded.
4) Social reinstatement
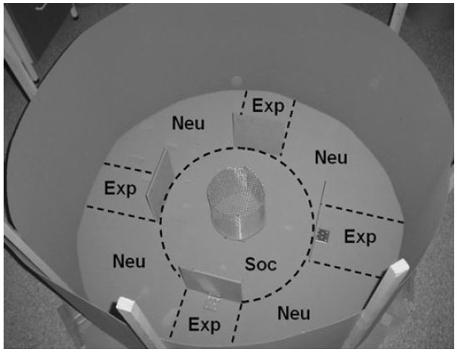
The need for social reinstatement was assessed by using a circular arena in the middle of which a holding pen was placed with two chicks in it. A third tested chick was placed on the border of the arena and I recorded the time the chick spent in the different areas of that arena (within 10 mn), meaning:
- The social area (soc), where the chick is close to conspecifics,
- The neutral area (neu), where the chick is further away from conspecifics but can still see them,
- The behind screen area (exp), where the chick cannot see its conspecifics.
Responsible for this page:
Director of undergraduate studies Biology
Last updated:
05/27/20
