Methods
1. Construction of GITRL and TWEAK expression vectors
Human full length GITRL and TWEAK DNA sequences were cloned into two pVax expression vectors at BamH1-EcoRI restriction site and (G: GITRL expressing plasmid and T: TWEAK expressing plasmid) were amplified to a concentration of 4mg/mL (GenScript Inc., USA).
2. Transient transfection and Western Blotting of the constructs
The DNA constructs were transfected in adherent vero cells (ATCC CRL-1587). Forty eight hours following the transfection, the cells were lysed by adding 1X Cell lysis buffer. Following a centrifugation at 14000rpm for 10 min, the supernatant were aspirated carefully and was loaded onto sodium dodecyl sulfate-10% polyacrylamide gels, electrophoresed at 120V and the proteins were transferred onto a nylon membrane (iBlot® transfer stacks, Invitrogen). After the addition of respective GITRL and TWEAK antibodies and the chemi luminescent substrate (ECL), the signal was developed onto X-ray film by autoradiography.
3. Mice and vaccinations
Female BALB/c mice that were 6-8 weeks old were purchased from Jackson laboratory (Indianapolis, IN). All the animals were housed in a temperature-controlled, light-cycled facility in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, USA) and the University of Pennsylvania Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). The experiments reported herein were conducted according to the principles set forth in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources, National Research Council, DHHS Publication number NIH-86-23 (1985).
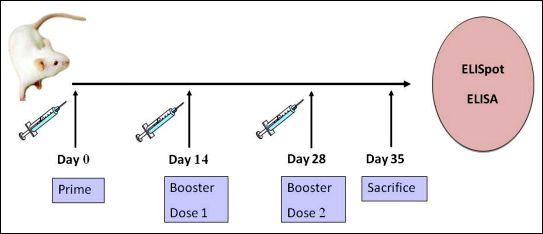
Note: 'D' denotes 15µg HIV-1 DNA
Ten groups of BALB/c mice (n=4 in each group) were immunized with various combinations of DNA vaccines as mentioned below: 15µg pVax (control), D, D+7.5µg G, D+7.5µg T, D+10µg G, D+10µg T, D+6µg G+4µg T, D+6µg T+4µg G and D+3.75µg G+3.75µg T respectively.
Following a prime, the quadriceps muscles of each hind limb were vaccinated at 14 th day and 21 st day with booster doses respectively. A total volume of 30µL was injected using an insulin syringe with a 29-gauge needle and delivery of DNA vaccine was done in vivo using Minimally Invasive Electroporation Delivery (MID-EP) system.
One week following each immunization, the mice were bled by retro-orbital bleeding method. In this method, a hemocrit tube was directed at a 45 degree angle to the eye socket, beneath the eye ball and by applying gentle pressure, the orbital sinus was broken and the blood was collected.
Seven days after the last immunization, the mice were sacrificed, the sera were collected and the spleen was isolated from the animals for immunological assays.
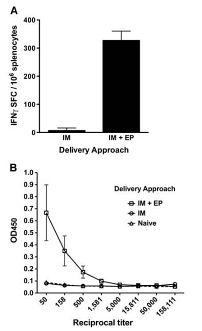
Electroporation method involves the application of short electrical pulses to the site of injection and this method was found to increase the transfection efficiency of DNA plasmid uptake by the cells, thus increasing the antigen production and immune responses following a vaccination. The graph indicated here shows the increased cellular response that was reported in a previous study, when electroporation was used as the delivery method.
4. Preparation of Splenocytes
The spleens were isolated from the mice and were processed into single cell suspensions in R10 medium in a Stomacher®80 machine (Steward Lab systems, UK).
5. Cellular response: ELI Spot assay
96-welled ELI Spot plates (Millipore) were coated with anti-mouse IFN-γ capture antibody and incubated overnight at 4 °C (R&D Systems, USA). Following the processing and counting of splenocytes, two hundred thousand splenocytes were added to each well and stimulated overnight with R10 medium (negative control), Con A ( concanavalin A - positive control), and specific antigenic peptides (10μg/ml; Invitrogen) respectively, in a 37°C incubator containing 5% CO2. The specific peptide pools that were used to stimulate the CD4+ and CD8+ T cells consisted of 15-mer peptides, that overlapped by 11 amino acids.
Following the incubation with biotinylated anti-mouse IFN-γ Abs and streptavidin–alkaline phosphatase (R&D Systems), 5-bromo-4-chloro-3′-indolylphosphate p-toluidine salt and nitro blue tetrazolium chloride (chromogen color reagent; R&D Systems) were added to each well. Once the color was developed, the plates were rinsed with distilled water and dried at room temperature. The spots were counted using an automated reader (ImmunoSpot II; Cellular Technologies Inc., Cleveland, OH).
6. Humoral immune response: antibody ELISA
To determine the HIV1-specific sera antibody titers, 96-well Nunc-Immuno MaxiSorp plates (Fisher Scientific 12-565-135) were coated overnight at 4°C with 1 μg/well of recombinant HIV-1 Clade C protein (Immune Technology, IT-001-CONCp) diluted in PBS. Plates were washed with PBS, 0.05% Tween 20 (PBST), blocked for one hour at room temperature with 10% BSA/PBST, and incubated with serial dilutions of serum from immunized or naļve animals for one hour at room temperature. Plates were then washed with PBST and goat anti-mouse IgG (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, SC-2055) was added at a dilution of 1:5,000 in PBST. Bound enzyme was detected by Sigma FAST O-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (OPD; Sigma-Aldrich, P1987), and the optical density was determined at 450 nm using Biotek EL312e Bio-Kinetics reader. All the serum samples were tested in triplicates.
Responsible for this page:
Director of undergraduate studies Biology
Last updated:
05/18/12
